Efficient Detection of Atrial Fibrillation
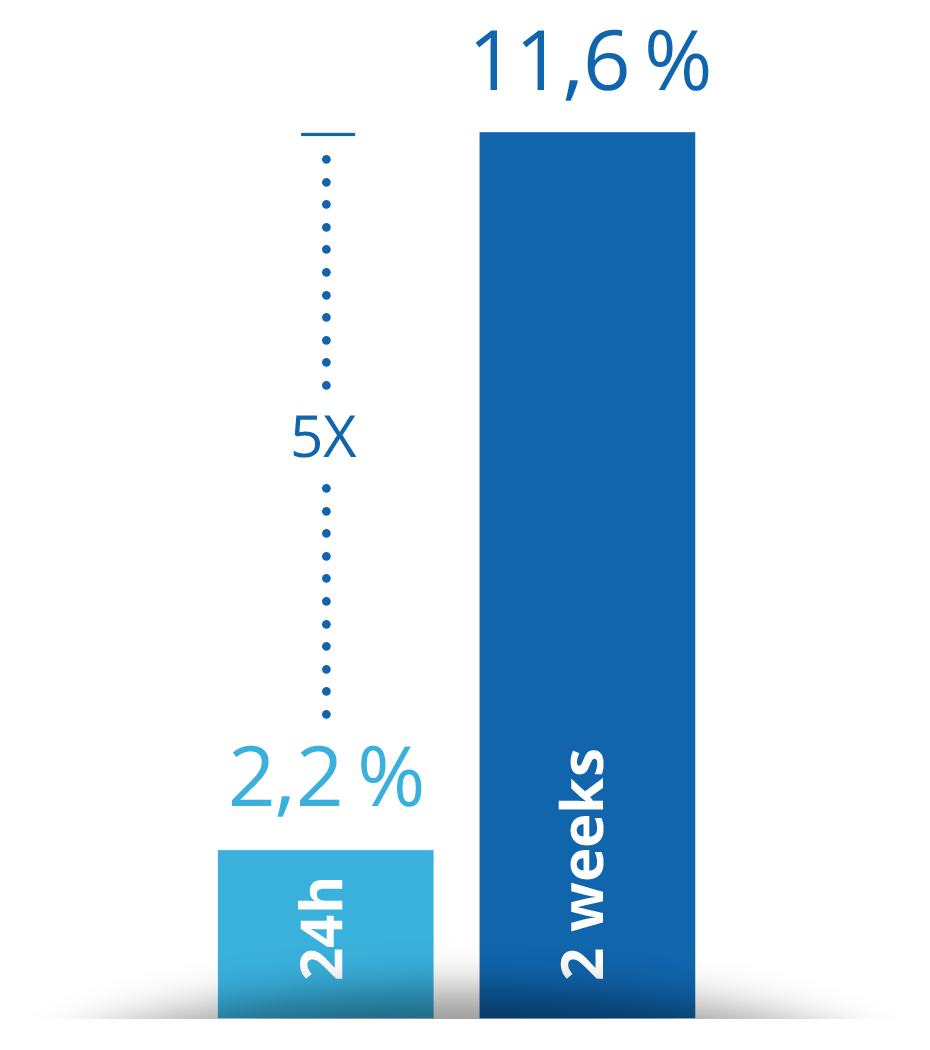
5-times more detection
14-day continuous monitoring allows to detect 5 times more cases of atrial fibrillation.
Gladstone, D.J, et al. Atrial Fibrillation in Patients with Cryptogenic Stroke. The new england journal of medicine, 2014.
PROLONGED CONTINOUS ECG MONITORING SIGNIFICANTLY INCREASES AF DETECTION
Atrial fibrillation (AF) is a common arrhythmia with increasing prevalence over time. It is associated with an increased risk of stroke. In patients in whom paroxysmal AF (PAF) is suspected, longer periods of monitoring will detect more cases of PAF.
DETECT AF AFTER CRYPTOGENIC STROKE OR TIA
Identification of AF is key to secondary stroke prevention. However, paroxysmal AF can be difficult to detect with conventional 24 to 48-hour Holter monitoring and is likely under-diagnosed in patients with stroke or transient ischemic attack (TIA). Prolonged ECG monitoring significantly increases the detection of AF.
CardioSTAT provides up to 14 days of continuous ambulatory ECG monitoring.
“The vast majority of patients with cryptogenic stroke/TIA should be investigated with prolonged heart rhythm monitoring of at least a few weeks.”
CardioSTAT Efficacy compared to Holter Monitor for Same Duration
CardioSTAT ambulatory ECG monitoring device in correlation with the standard Holter ECG monitoring for detection of AF, of AV block and of pauses over 24 hours monitoring.
Dr Nault, I. et al., Validation of a novel single lead ambulatory ECG monitor – CardioSTAT™ – Compared to a standard ECG Holter monitoring. Journal of Electrophysiology, 2019.